Invented by James G. Fujimoto, Adolf F. Fercher, Christoph K. Hitzenberger, David Huang, and Eric A. Swanson, Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT scan) was patented at MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology) in 1991. According to the National Academy of Engineering, these inventors were awarded the 2017 Fritz J. and Dolores H. Russ Prize which recognizes a bio-engineering achievement that significantly improves the human condition, cites OCT for “leveraging creative engineering to invent imaging technology essential for preventing blindness and treating vascular and other diseases”.
The OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) is one of the most widely used technologies for imaging in the human eye and may be used to aid in the treatment and early detection of blinding diseases and eye conditions – some of these conditions include:
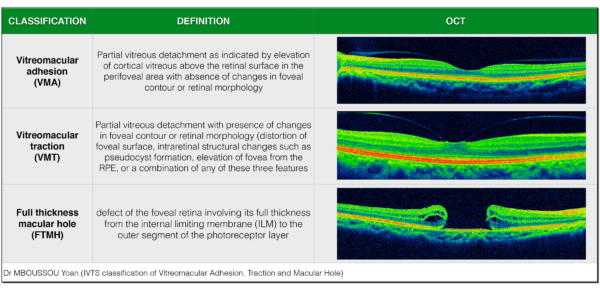
- Macular edema
- Macular hole
- Macular pucker
- Age-related macular degeneration
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Central serous retinopathy
- Glaucoma
How OCT Works
Optical Coherence Tomography functions similar to an ultrasound system but with higher resolution and is a non-invasive diagnostic instrument that relies on light waves to capture images of the tissue layers within the retina. These images are extremely high-definition, volumetric 3D scans that detail various layers of the eye, and provide doctors with information that makes it easier to diagnosis and treat eye conditions.
During an OCT exam, your ophthalmologist may use dilating eye drops in your eyes to widen your pupil, making it easier to examine the retina. When testing for glaucoma and macular degeneration, pupil dilation may not be necessary. The baseline OCT test takes approximately 10 minutes and repeat scans typically take less than five minutes.
With these highly detailed images, your ophthalmologist is able to identify anomalies in ocular structures and detect diseases that may threaten your eye sight. A totally safe and harmless procedure, OCT is also beneficial in monitoring the treatment of glaucoma and other retinal diseases.
During an OCT exam, your ophthalmologist may use dilating eye drops in your eyes to widen your pupil, making it easier to examine the retina.
featured image credits: By Yoanmb – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, Link